-
- 15383190639
- admin@86-ss.com
Your Location:Home >Products >Organic chemicals >527-07-1

Product Details
|
Concrete Admixture |
Sodium gluconate (SG) is used as a retarding admixture in concrete, affecting the setting and hardening behaviors of cement. Even at very small dosages, SG can significantly influence the properties of concrete. In concrete engineering, SG is commonly used as an organic retarding admixture. It exhibits a significant retarding effect, good adaptability with superplasticizer systems, and is cost-effective compared to other additives. |
|
Biostimulant |
SG has been identified as a biostimulant that enhances the efficiency of the degradation of B[a]p (benzo[a]pyrene), a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. |
|
Geopolymer Application |
Sodium gluconate is utilized in the preparation of geopolymers, particularly in conjunction with sewage sludge ash (SSA), aiming to utilize sewage sludge resources. The addition of SG inhibits the setting time of geopolymers, delaying the initial setting time significantly. This delay is attributed to SG interfering with the dissolution of precursor materials and the growth of hydration gel, affecting the early hardening process. Environmental and economic analyses suggest that delaying the setting of geopolymers through SG inclusion is a favorable option compared to altering alkali activators. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Sodium gluconate is an organic sodium salt having D-gluconate as the counterion. It has a role as a chelator. It contains a D-gluconate. |
|
Production Methods |
Sodium gluconate is manufactured by the fermentation of carbohydrate containing the raw material glucose syrup derived from maize. After a crystallisation step, sodium gluconate is separated from the mother liquor by centrifugation, the crystals are dried and then sieved to guarantee the desired granulation. Based on the production process as well as the raw materials used, sodium gluconate is not synthetic natural. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Electrolyte replenisher |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Ingestion of sodium gluconate is known to stimulate the production of intestinal butyrate. It is widely used in food, pharmaceutical paper and textile industry. It acts as a chelating agent. Sodium gluconate serves as a detergent in bottle washing formulation. |
|
Safety Profile |
Low toxicity by intravenous route. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes |
|
Synthesis |
The calcium gluconate is added into the reaction kettle. Add sulfuric acid aqueous solution while stirring. After mixing for one hour, let it stand for a while and then get it filtered. The filter residue is CaSO4 and gets it removed. The filtrate is added into the neutralization kettle, and a proper amount of Na2CO3 aqueous solution is added to neutralize it. Finally get sodium gluconate through concentration, filtration and drying. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise it from a small volume of H2O (solubility is 59g/100mL at 25o), or dissolve it in H2O and add EtOH since it is sparingly soluble in EtOH. It is insoluble in Et2O. It forms a Cu complex in alkaline solution and a complex with Fe in neutral solution. [cf p 639, Sawyer & Bagger J Am Chem Soc 81 5302 1959, Beilstein 3 I 188.] |
|
Regulations |
In Europe, sodium gluconate is listed as a generally permitted food additive (E576) and may be added to all foodstuffs, following the "quantum satis" principle, as long as no special regulation restricts the use.The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) assigned sodium gluconate the “generally recognised as safe” (GRAS) status and permitted its use in food without limitation other than current good manufacturing practice.Sodium gluconate is exempted from the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) by means of Commission Regulation (EC) No. 987/2008 of 8 October, 2008 (amending Annex IV). As a consequence thereof, there is no need to register sodium gluconate. |
InChI:InChI=1/C14H14O3.C6H12O7.Na/c1-8(2)7-11(15)12-13(16)9-5-3-4-6-10(9)14(12)17;7-1-2(8)3(9)4(10)5(11)6(12)13;/h3-6,8,12H,7H2,1-2H3;2-5,7-11H,1H2,(H,12,13);/q;;+1/p-1/t;2-,3-,4+,5-;/m.1./s1
The laccase-mediator system (LMS) for th...
Gold nanoparticles (NPs) with mean diame...
The application of synthetic flavinium o...
Abstract: Gold nanoparticles (NPs) with ...
A fast and efficient methodology for the...
N-(n-octyl)-6-deoxy-D-gluconamide crysta...
The effect of the reduction method on th...
Maltodextrins were oxidized to polyglucu...
Unprotected aldoses in water undergo an ...
A bio-inspired approach for efficient co...
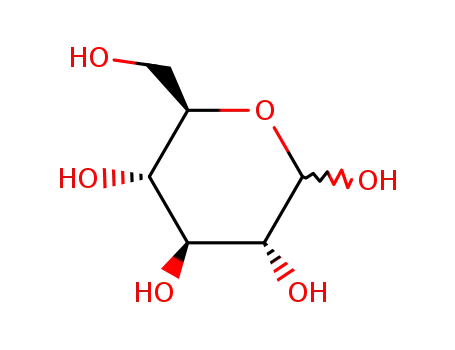
D-Glucose

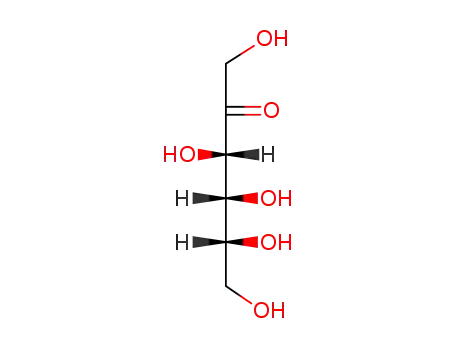
D-Fructose
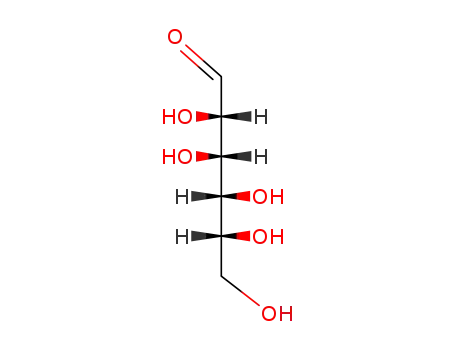
D-Mannose

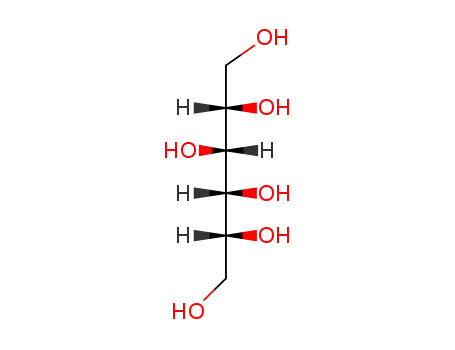
D-sorbitol

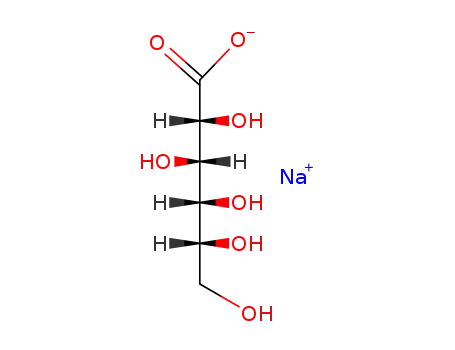
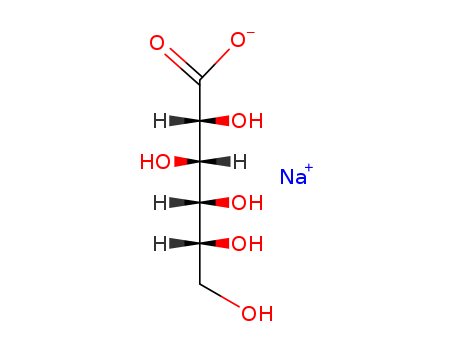
sodium D-gluconate

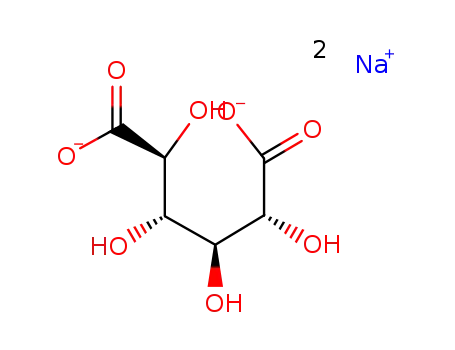
D-glucaric acid disodium salt

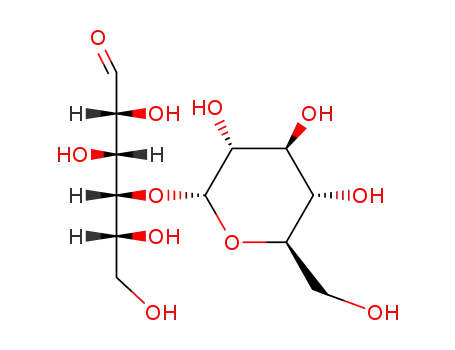
D-maltose
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide; sodium hydroxide;
In
water;
at 50 - 60 ℃;
Sealed tube;
|
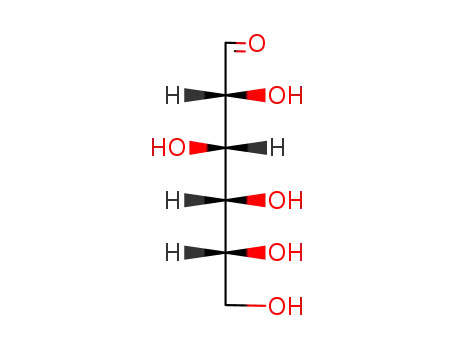
D-glucose

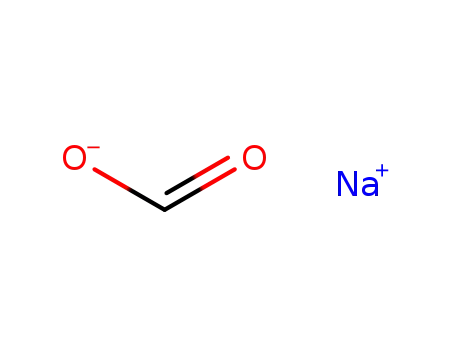
sodium formate

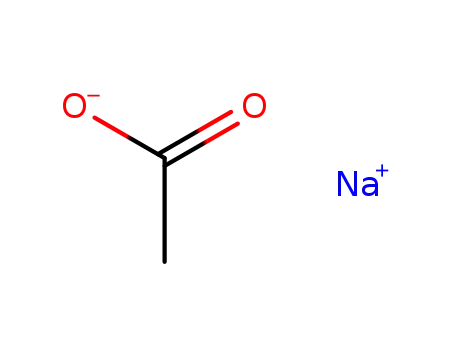
sodium acetate

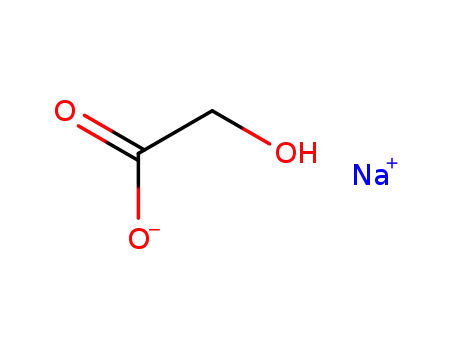
sodium glycolate


sodium D-gluconate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
oxygen; sodium hydroxide;
at 150 ℃;
for 2h;
under 15001.5 Torr;
Reagent/catalyst;
Autoclave;
|
38.14% 5.67% 7.7% 9.83% |

D-glucose

D-Glucose
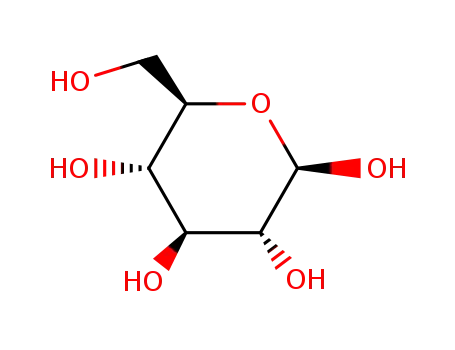
β-D-glucose
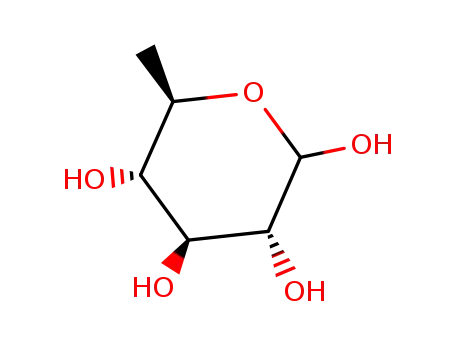
6-deoxy-D-glucose
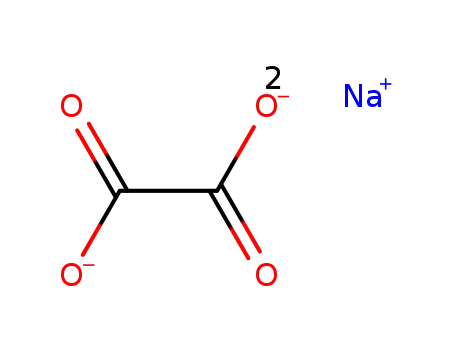
sodium oxalate
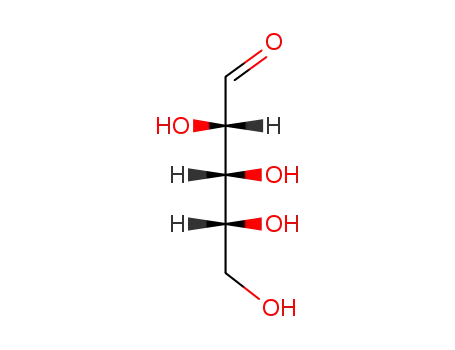
D-Arabinose
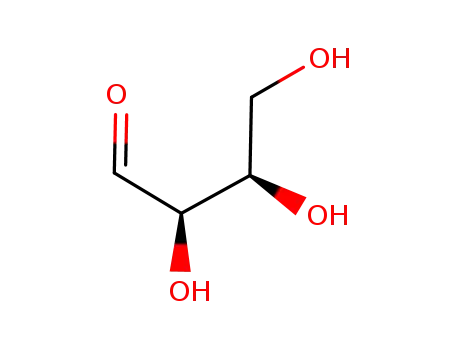
D-erythrose
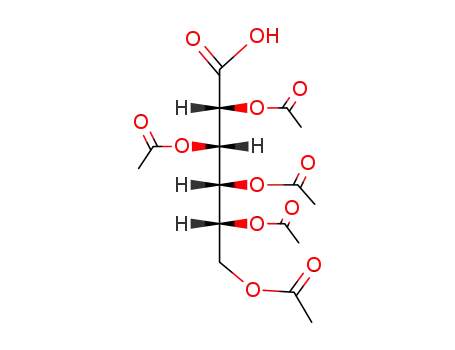
penta-O-acetyl-D-gluconic acid
CAS:9005-38-3
CAS:29923-31-7
CAS:57-50-1
CAS:77-93-0