-
- 15383190639
- admin@86-ss.com
Your Location:Home >Products >Organic chemicals >5329-14-6

Product Details
|
Reactions |
Sulfamic acid is a strong acid that reacts with many basic compounds. It is heated to above the melting point (209°C) under normal pressure to begin to decompose, and continues to be heated to above 260°C to decompose into sulfur trioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen and water.(1) Sulfamic acid can react with metals to form transparent crystalline salts. Such as:2H2NSO3H+Zn→Zn(SO3NH2)2+H2.(2) Can react with metal oxides, carbonates and hydroxides:FeO+2HSO3NH2→Fe(SO3NH2)2+H2O2CaCO3+2HSO3NH2→Ca(SO3NH2)2+H2O+CO23Ni(OH)2+2HSO3NH2→Ni(SO3NH2)2+H2O.(3) Can react with nitrate or nitrite:HNO3+HSO3NH2→H2SO4+N2O+H2O2HNO2+HSO3NH2→H2SO4+N2+H2O.(4) Can react with oxidants (such as potassium chlorate, hypochlorous acid, etc.): KClO3+2HSO3NH2→2H2SO4+KCl+N2+H2O22HOCl+HSO3NH2→HSO3NCl2+2H2O |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Moderately soluble in water [Hawley]. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Sulfamic acid reacts exothermically with bases. Aqueous solutions are acidic and corrosive. |
|
Hazard |
Toxic by ingestion. |
|
Health Hazard |
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A human skin irritant. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. A substance that migrates to food from packaging materials. Violent or explosive reactions with chlorine, metal nitrates + heat, metal nitrites + heat, fuming HNO3. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx and NOx. See also SULFONATES. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Sulfamic acid is used in metal and ceramic cleaning, bleaching paper pulp; and textiles metal; in acid cleaning; as a stabilizing agent for chlorine and hypochlorite in swimming pools; cooling towers; and paper mills. |
|
Shipping |
UN2967 Sulfamic acid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise NH2SO3H from water at 70o (300mL per 25g), after filtering, by cooling a little and discarding the first batch of crystals (about 2.5g) before standing in an ice-salt mixture for 20minutes. The crystals are filtered off by suction, washed with a small quantity of ice cold water, then twice with cold EtOH and finally with Et2O. Dry it in air for 1hour, then store it in a desiccator over Mg(ClO4)2 [Butler et al. Ind Eng Chem (Anal Ed) 10 690 1938]. For the preparation of primary standard material see Pure Appl Chem 25 459 1969. |
|
Incompatibilities |
The aqueous solution is a strong acid. Reacts violently with strong acids (especially fuming nitric acid), bases, chlorine. Reacts slowly with water, forming ammonium bisulfate. Incompatible with ammonia, amines, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin, oxidizers. |
|
Application |
Sulfamic acid, the monoamide of sulfuric acid, is a strong inorganic acid. It is generally used in chemical cleaning processes like removal of nitrites, carbonate- and phosphate-containing deposits.Sulfamic acid can be used as a catalyst in:Friedlander quinoline synthesis.Liquid Beckmann rearrangement for the synthesis of amides from ketoximes.The preparation of α-aminophosphonates via a three-component reaction between aldehydes, amines, and diethyl phosphite. |
|
Definition |
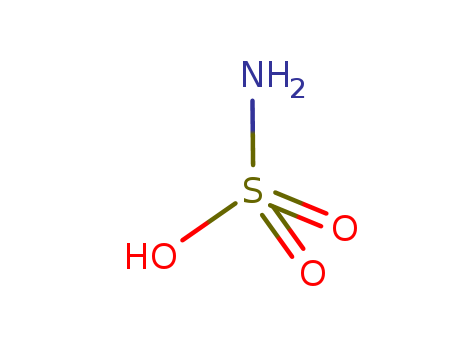
ChEBI: Sulfamic acid is the simplest of the sulfamic acids consisting of a single sulfur atom covalently bound by single bonds to hydroxy and amino groups and by double bonds to two oxygen atoms. It is a strong acid, readily forming sulphamate salts, which is extremely soluble in water and normally exists as the zwitterion H3N+. SO3–. |
|
General Description |
Sulfamic acid appears as a white crystalline solid. Density 2.1 g / cm3. Melting point 205°C. Combustible. Irritates skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Low toxicity. Used to make dyes and other chemicals. It is used as a raw material for the preparation of a synthetic sweetener i.e, sodium cyclohexylsulfamate. |
InChI:InChI=1/H3NO3S/c1-5(2,3)4/h(H3,1,2,3,4)
The kinetics of the gas phase reaction S...
A new mixed-valent Rh2II,III dimer, [Rh ...
The kinetics of hydrolysis at medium aci...
A process for making an N1-(2′-pyridyl)-...
Compounds having kappa opioid agonist ac...
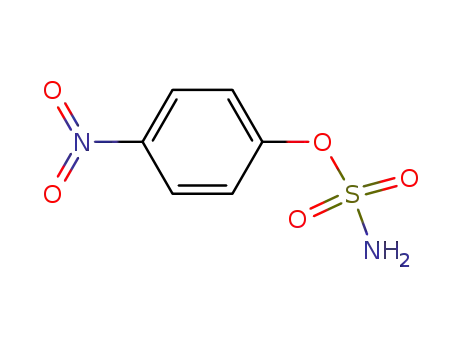
4-nitrophenyl sulfamate

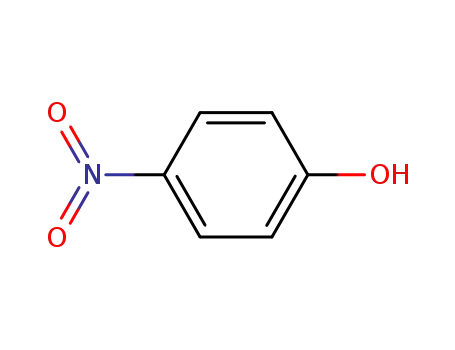
4-nitro-phenol
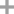
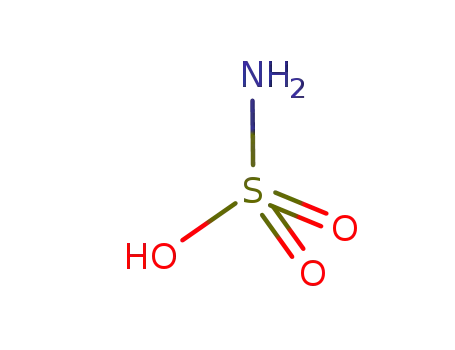
aminosulfonic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water;
In
acetonitrile;
at 20 ℃;
pH=11.7;
pH-value;
Temperature;
Activation energy;
Mechanism;
|
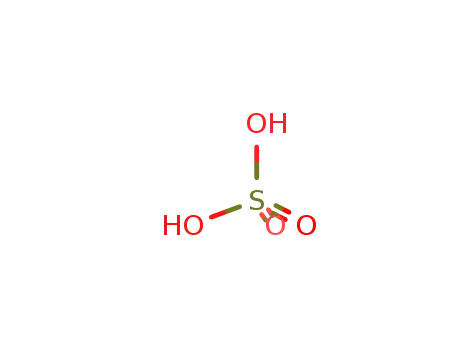
sulfuric acid

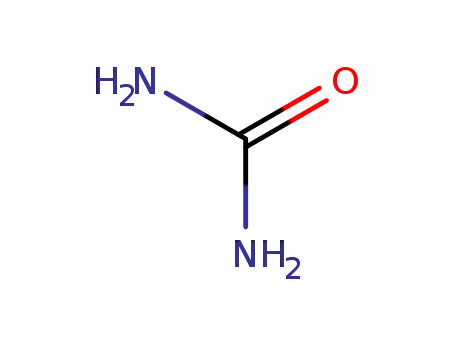
urea

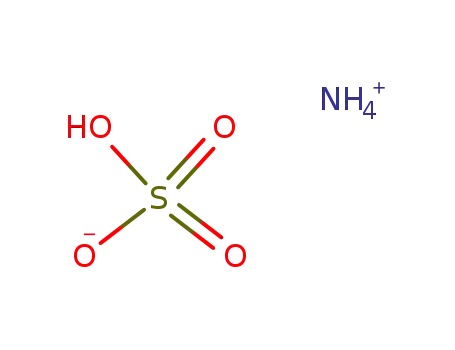
ammonium bisulfate


aminosulfonic acid

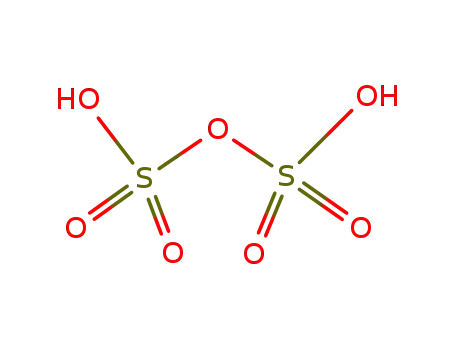
disulfuric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
sulfuric acid;
byproducts: CO2; heating with excess H2SO4 (100%/130-140°C); evolution of CO2;;
|
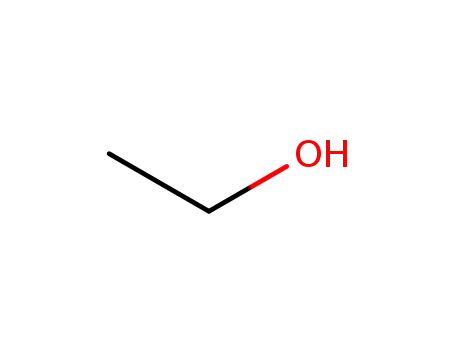
ethanol
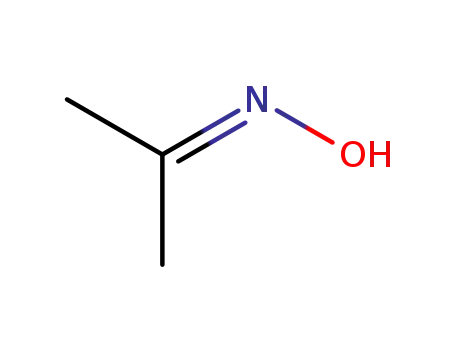
acetone oxime
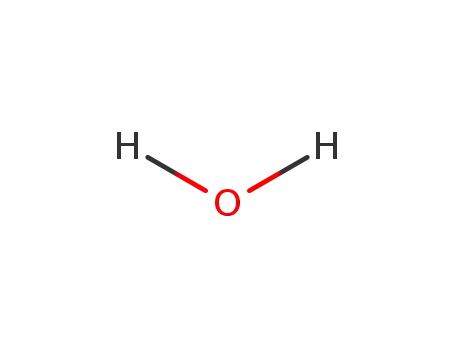
water
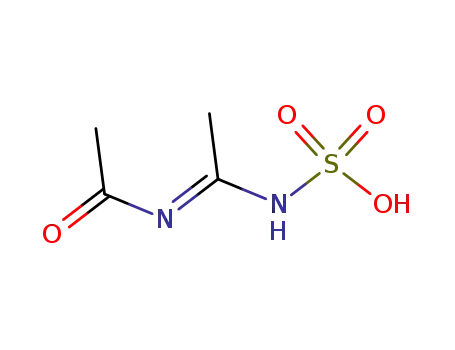
(N-acetyl-acetimidoyl)-amidosulfuric acid
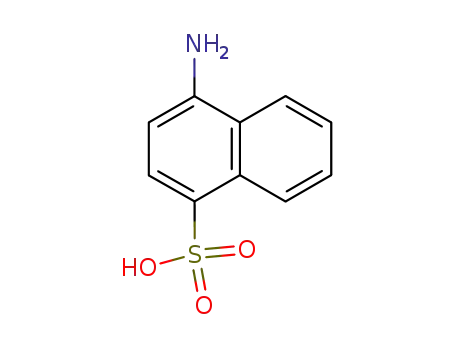
4-amino-1-naphthalenesufonic acid
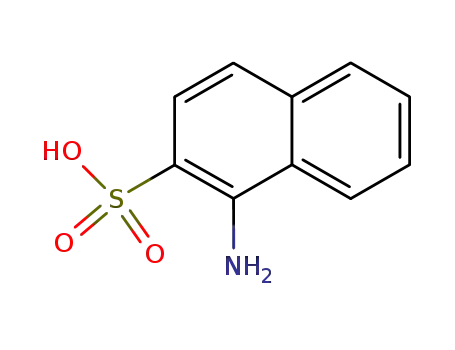
1-aminonaphthalene-2-sulfonic acid
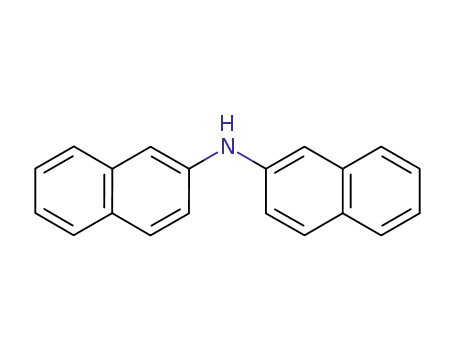
2,2'-dinaphthylamine
4-aminobenzene sulfonic acid
CAS:10039-54-0
CAS:274693-27-5
CAS:142-82-5
CAS:512-04-9