-
- 15383190639
- admin@86-ss.com
Your Location:Home >Products >Pharmaceutical intermediate >86386-73-4
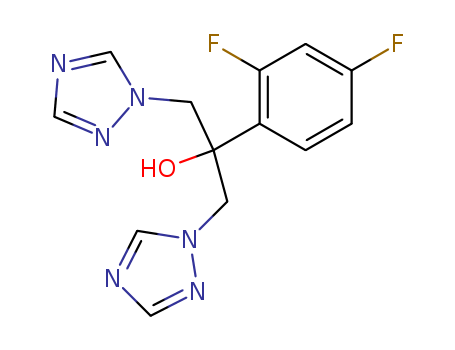

Product Details
|
Anti-fungal infection drug |
Fluconazole-D4 is a novel kind triazole drug of anti-fungal infection which was first successfully developed by the American Pfizer with broad-spectrum anti-fungal effect. It belongs to a kind of systemic anti-fungal products and has high selectivity on the inhibitory effect of the fungal cytochrome P450-dependent enzyme. It is also a kind of potent and specific inhibitor for the fungi alcohol synthesis. Clinically it is mainly used for the treatment of vaginal candidiasis, thrush, atrophic oral candidiasis, fungal meningitis, pulmonary fungal infections, abdominal infections, urinary tract infections and skin fungi infection. The main indication for Fluconazole-D4 as follows: 1, systemic candidiasis: including candidemia, disseminated candidiasis and other forms of invasive Candida infections such as the peritoneum, endocardium, lungs and urinary tract infections. It can also be applied to patients of malignant tumors, special-care patients, patients who received radiotherapy, chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy as well as patients who are susceptible to other factors such as infection of Candida. It can also be used for prevention of the occurrence of candida infection for bone marrow transplant patients upon receiving cytotoxic drugs treatment or radiation treatment. 2, cryptococcosis: including cryptococcal meningitis and the cryptococcal infection in other parts (such as lung, skin). It can be applied to the patient of normal immune function, AIDS patients as well as patient of suppressed immune function due to organ transplant and other reasons. AIDS patients can administer this kind of drug for maintenance therapy and prevention of the relapse of cryptococcal disease. 3, mucosal candidiasis: including oropharyngeal, esophageal, non-invasive bronchial mucosal candidiasis, pulmonary candidiasis, Candida urine disease, mucocutaneous and chronic atrophic oral candidiasis. It can be applied to patients of both normal immune function and with impaired immune function. 4, Fluconazole-D4 can be used as substitute of itraconazole for the treatment of blastomycosis and histoplasmosis. 5, it can be used for the treatment of acute or recurrent vaginal candidiasis. 6, for leukemia patients or patients of other malignant tumor who is susceptible to fungal infection upon undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy can apply it as means of preventive treatment. 7, it can be used for the treatment coccidioidomycosis. 8, it can be used for treatment of fungal skin disease including fungal skin infections such as body ringworm, tinea pedis, tinea versicolor, tinea capitis, onychomycosis and nail ringworm. 9, Fluconazole-D4 can also be used for the treatment of skin chromomycosis. In August 2002, the voriconazole (Pfizer) which enters in the United States is the further structural modified derivative of Fluconazole-D4 with its antibacterial activity against pathogenic yeast being higher than fluconazole. Some case reports have demonstrated that the drug can successfully cure some rare fungal disease. |
|
Production method |
Method 1: From reaction between the formamide, hydrazine hydrate and 85% formic acid, we can obtain 1H-1, 2, 4-triazole. From phenylenediamine, we can obtain difluorobenzene, which is further subject to bromination to generate 2, 4-difluoro-bromobenzene. Magnesium was dissolved in anhydrous diethyl ether and added drop wise of the diethyl ether solution of 2, 4-difluoro-bromobenzene under ultrasonic irradiation, followed by adding drop wise of the diethyl ether solution of 1, 3-dichloroacetone under ice-cooling condition. Stir at room temperature overnight. Add glacial acetic acid and water. The separated organic layer was dried and concentrated. Concentrate, triazole, potassium carbonate and PEG600 were dissolved in anhydrous ethyl acetate and were subject to reflux. Then filter, wash with water to neutralization and dryness. The solvent was distilled off and was further subject to cyclohexane-ethyl acetate (1: 1) recrystallization to obtain the fluconazole with the overall yield being 33.6% and the m.p. being 138.5-140 ℃. The last step can also be carried out in propionitrile. 1, 3-dihalo (x = Br or Cl)-2-(2, 4-difluorophenyl)-2-propanol and 1H-1, 2, 4-triazol-propionitrile were put into propionitrile and subject to reflux under the catalysis of sodium hydroxide and PEG 600 phase transfer catalysis and obtain the fluconazole crude product. The crude product was dissolved in fatty alcohols (such as propanol, isopropanol or butanol, etc.), dissolved upon heating with a small amount of active carbon for decoloring and then cooled to give crystals which is the refined product of fluconazole with the melting point being 139~140 ℃. Method 2:2: 2, 4-difluorophenyl methyl is reacted with the Grignard reagent of 1-chloromethyl-1, 2, 4-triazole, and hydrolyzed to obtain fluconazole. Method 3: difluorophenyl is subject to bromination to generate 1-bromo-2, 4-difluorobenzene, and then further converted to Grignard reagent. The resulting Grignard reagent above is reacted with 1, 3-bis (1H-1, 2, 4-triazole group) acetone, followed by hydrolysis to give fluconazole. |
|
Indications |
Fluconazole (Diflucan) may be better absorbed and is possibly less hepatotoxic than ketoconazole, but it is considerably more expensive, an important consideration given the required length of therapy for most cutaneous fungal diseases. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
141.1 g of aluminum trichloride was first added to 86 ml of DFB and 77 ml of chloroacetyl chloride was then added to the mixture, which was allowed to react at 60°C for 3 hours. After the reaction mixture had cooled down, 500 g of cold water was added. The mixture was stirred for about 20 min and then filtered to afford about 158.5 g of 2-chloro-2',4'-difluoroacetophenone in solid form (91% yield).A solution of 158.5 g of 2-chloro-2',4'-difluoroacetophenone and 88.8 g of 4- amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole in 1,600 ml of cyanomethane was heated at reflux for 16 hours, cooled down, and filtered. The solid thus obtained was then washed with 500 ml of ethyl ether once to afford 2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2',4'- difluoroacetophenone salt.The crude product obtained was dissolved in 1,320 ml of 1.5 N hydrochloric acid. To the solution thus obtained, an aqueous solution (330 ml) of sodium nitrite (58.2 g) was dropwise added and the mixture was allowed to react for 30 min. Aqueous ammonium was then used to adjust the reaction mixture to a neutral pH. The solid was precipitated and filtered to afford 159 g of 2-(1H- 1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2',4'-difluoroacetophenone (yield about 80%), which had a water content of about 10%.4 g of 4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole, 57.87 g of potassium hydroxide, 118 g of trimethyl sulfoxonium iodide, and 100 g of 2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-l-yl)-2',4'- difluoroacetophenone were dissolved in 1,600 ml of water. The solution was heated at 70°C to react for 16 hours. Upon the completion of the reaction, the solution was adjusted with 4 N hydrochloric acid to a neutral pH and then extracted with acetyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, dried with 30 g of anhydrous calcium dichloride, decolorized with 15 g of active charcoal, and finally filtered off solid residues. The filtrate was concentrated to afford 99.3 g of the crude product (yield 72%). The crude product was further recrystallized from 500 ml of a solvent mixture of acetyl acetate and n-hexane (2:1) to afford 66.3 g of the Fluconazole in the form of white solid (yield 48%). |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antifungal |
|
Antimicrobial activity |
The spectrum is limited, but includes most Candida spp., Cryptococcus spp., dermatophytes and dimorphic fungi (Blast. dermatitidis, Coccidioides spp., Hist. capsulatum and Paracoccidioides brasiliensis). Strains of C. krusei appear to be insensitive. |
|
Acquired resistance |
Resistant strains of C. albicans have been isolated from AIDS patients given long-term treatment for oral or esophageal candidosis. Strains of C. glabrata frequently become resistant during short courses of treatment. There are a few reports of fluconazole-resistant strains of Cryp. neoformans recovered from AIDS patients with relapsed meningitis. Most, but not all, C. albicans and C. glabrata strains resistant to fluconazole are cross-resistant to other azoles. |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
A synthetic bis(triazole) available for oral or parenteral administration. A prodrug formulation, fosfluconazole, is available for intravenous use in Japan. |
|
Biological Activity |
Triazole antifungal agent. Effective against Candida strains in vitro and in vivo . |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Fluconazole is an antifungal agent. It is highly selective inhibitor of fungal cytochrome P-450 sterol C-14 α-demethyllation. Fluconazole is a potent inhibitor of CYP2C9. Fluconazole interferes with fungal ergosterol synthesis and downregulates the metallothionein gene. |
|
Pharmacology |
It has good oral absorption, is well tolerated, and is preferentially taken up in keratinized tissues, reaching concentrations up to 50 times that in plasma. This allows for once-weekly dosing in most cases. |
|
Pharmacokinetics |
Oral absorption: >93% Cmax 50 mg oral: c. 1 mg/L after 2 h Plasma half-life: 25–30 h Volume of distribution: 0.6–0.8 L/kg Plasma protein binding; <10% Absorption Oral absorption is rapid (1–3 h) and is not affected by food or intragastric pH. Blood concentrations increase in proportion to dosage. Maximum serum concentrations increase to about 2–3 mg/L after repeated dosing with 50 mg. Distribution It is widely distributed, achieving therapeutic concentrations in most tissues and body fluids. Concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are 50–60% of the simultaneous serum concentration in normal individuals and even higher in patients with meningitis. Metabolism and excretion More than 90% of an oral dose is eliminated in the urine: about 80% as unchanged drug and 10% as inactive metabolites. The drug is cleared by glomerular filtration, but there is significant tubular reabsorption. The plasma half-life is prolonged in renal failure, necessitating adjustment of the dosage.Fluconazole-D4 is removed during hemodialysis and, to a lesser extent, during peritoneal dialysis. In children the volume of distribution and plasma clearance are increased, and the half-life is considerably shorter (15–25 h). |
|
Side effects |
Fluconazole is well tolerated. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and skin rash have been reported in fewer than 3% of patients. Asymptomatic liver enzyme elevation has been described, and several cases of drugassociated hepatic necrosis have been reported. Alopecia has been reported as a common adverse event in patients receiving prolonged high-dose therapy. Coadministration of fluconazole with phenytoin results in increased serum phenytoin levels. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Fluconazole may have use in veterinary medicine in the treatment of systemic mycoses, including cryptococcal meningitis, blastomycosis, and histoplasmosis. It may also be useful for superficial candidiasis or dermatophytosis. Because of the drug’s unique pharmacokinetic qualities, it is probably more useful in treating CNS infections or fungal urinary tract infections than other azole derivatives. Fluconazole does not have appreciable effects (unlike ketoconazole) on hormone synthesis and may have fewer side effects than ketoconazole in small animals. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Aminophylline: concentration of aminophylline possibly increased. Analgesics: increases concentration of celecoxib - halve celecoxib dose; concentration of flurbiprofen, ibuprofen and methadone increased; increases concentration of parecoxib - reduce parecoxib dose; inhibits metabolism of alfentanil; concentration of fentanyl possibly increased. Anti-arrhythmics: avoid concomitant use with amiodarone due to risk of QT prolongation. Antibacterials: avoid with erythromycin; increases rifabutin levels - reduce dose; metabolism accelerated by rifampicin; concentration of bedaquiline possibly increased - avoid if fluconazole for >14 days. Anticoagulants: potentiates effect of coumarins. Antidepressants: avoid concomitant use with reboxetine; concentration of amitriptyline and nortriptyline increased. Antidiabetics: possibly enhances hypoglycaemic effect of nateglinide; increases concentration of sulphonylureas. Antiepileptics: increases fosphenytoin and phenytoin levels; possibly increased carbamazepine concentration. Antimalarials: avoid concomitant administration with artemether/lumefantrine and piperaquine with artenimol. Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with pimozide - avoid concomitant use; possibly increases lurasidone concentration; possibly increased quetiapine levels - reduce dose of quetiapine. Antivirals: increases nevirapine, ritonavir, tipranavir and zidovudine levels, and possibly saquinavir: concentration of simeprevir possibly increased - avoid. Anxiolytics and hypnotics: increases diazepam and midazolam levels. Avanafil: concentration of avanafil possibly increased. Bosentan: increased bosentan levels - avoid concomitant use. Ciclosporin: increases blood/serum ciclosporin levels. Clopidogrel: possibly reduced antiplatelet effect. Cytotoxics: possibly increased side effects of cyclophosphamide; concentration of bosutinib and possibly olaparib increased - avoid or reduce dose of bosutinib; possibly increases ibrutinib concentration - reduce ibrutinib dose; reduce dose of ruxolitinib. Dapoxetine: reduce dose of dapoxetine. Diuretics: increased eplerenone levels - avoid concomitant use; concentration of fluconazole increased by hydrochlorothiazide. Ergot alkaloids: increased risk of ergotism - avoid concomitant use. Guanfacine: possibly increased guanfacine dose - halve dose of guanfacine. Ivabradine: increased ivabradine levels - reduce initial dose. Ivacaftor: increased concentration of ivacaftor. Lipid-lowering drugs: possibly increased risk of myopathy with atorvastatin or simvastatin; concentration of fluvastatin increased possibly increased risk of myopathy; avoid with lomitapide. Retinoids: possibly increased risk of tretinoin toxicity. Sirolimus: may increase sirolimus concentration. Tacrolimus: increases blood/serum tacrolimus levels. Theophylline: possibly increases theophylline levels. |
|
Metabolism |
Fluconazole is metabolised only to a minor extent. Of a radioactive dose, only 11% is excreted as metabolites in the urine. The major route of excretion is renal, with approximately 80% of the administered dose appearing in the urine as unchanged medicinal product. Fluconazole clearance is proportional to creatinine clearance. There is no evidence of circulating metabolites. |
|
Brand name |
Diflucan (Pfizer). |
|
General Description |
Fluconazole is used to treat adult neutropenic patients with invasive candidiasis (IC). |
InChI:InChI=1/C13H12F2N6O/c14-10-1-2-11(12(15)3-10)13(22,4-20-8-16-6-18-20)5-21-9-17-7-19-21/h1-3,6-9,22H,4-5H2
A novel complex of copper(II) was prepar...
The application of continuous methods in...
Fluconazole and a series of 2-(2,4-diflu...
Methods of synthesizing compounds compri...
A scalable procedure for the direct prep...
The invention discloses a preparation me...
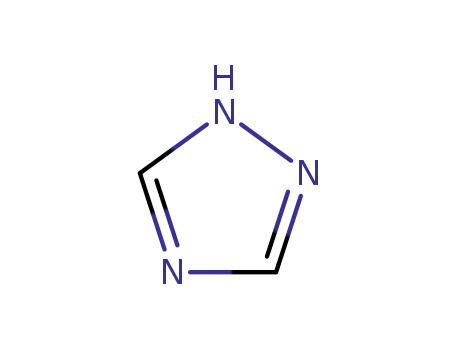
1,2,4-Triazole
![1-[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2,3-epoxypropyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole](/upload/2024/11/456a52ed-82a8-47a1-ac4a-5ae017e0ef32.png)
1-[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2,3-epoxypropyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole

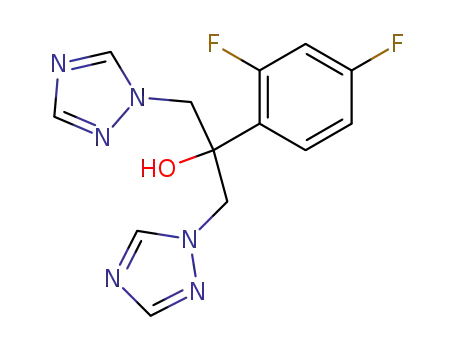
fluconazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
potassium carbonate;
In
acetonitrile;
at 60 ℃;
|
68.1% |
|
With
potassium carbonate;
In
isopropyl alcohol;
at 75 ℃;
for 16h;
|
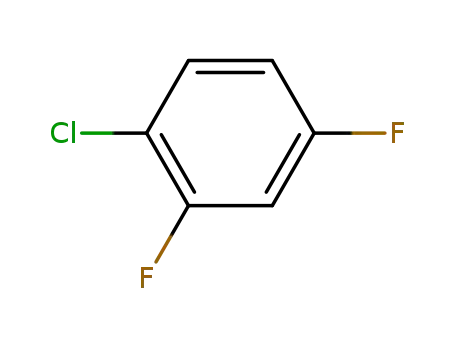
1-chloro-2,4-difluorobenzene

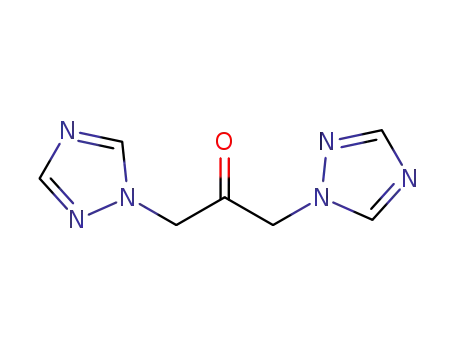
1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propanone


fluconazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
1-chloro-2,4-difluorobenzene;
With
iodine; magnesium; lithium chloride;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran;
at 40 - 50 ℃;
for 3h;
1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propanone;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran;
at 20 - 40 ℃;
for 2h;
|
96.1% |

1,2,4-Triazole
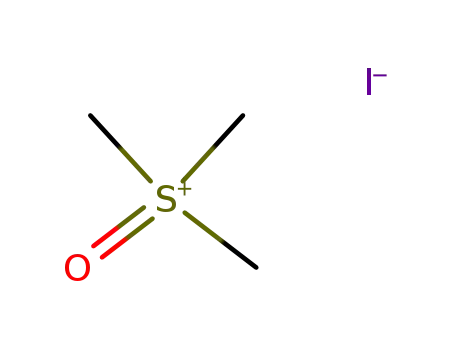
trimethylsulfoxonium iodide
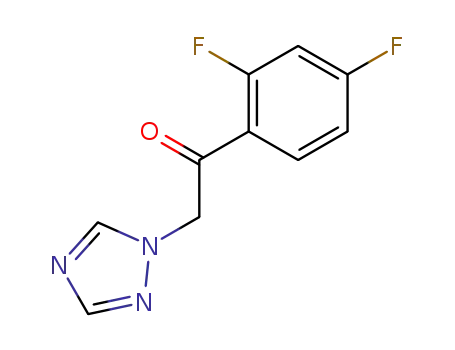
1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazolyl)ethanone
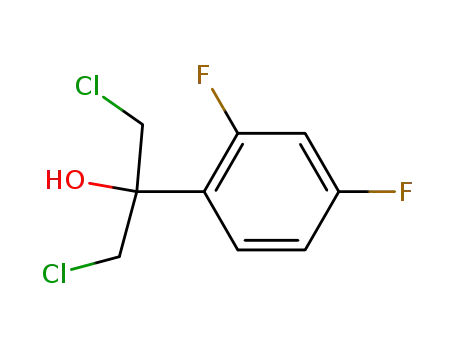
1,3-(dichloro)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)propan-2-ol
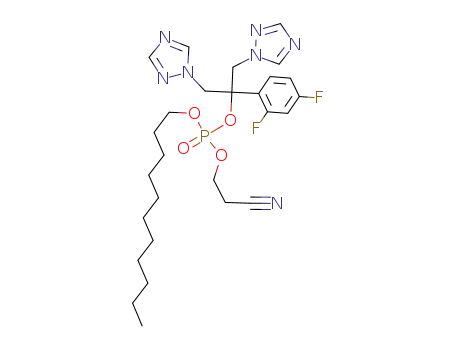
2-cyanoethyl-n-undecanyl fluconazole phosphate
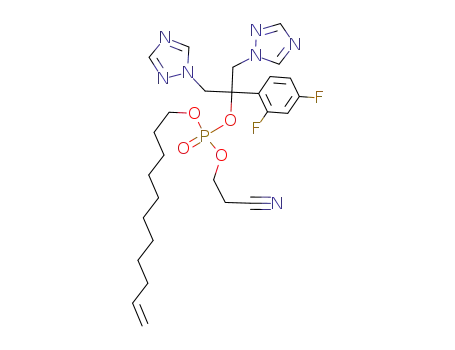
2-cyanoethyl-ω-undecenyl fluconazole phosphate
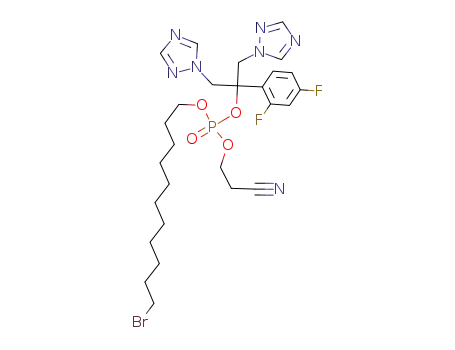
11-bromoundecanyl-2-cyanoethyl fluconazole phosphate
CAS:274693-27-5
CAS:85070-48-0
CAS:11138-66-2
CAS:74163-84-1